What careers are there in space and how do you get started?
Our Mission: Demystify the Space Sector
We’ve said it before, and we’ll say it again; Space isn’t all Astronauts and Rocket Scientists.
There are thousands of different roles in the space sector, and whilst STEM leads the way, there truly is a place for everyone.
Considering a Career in STEM?
The space sector is a fascinating and rapidly growing industry that offers a multitude of career opportunities for professionals with different backgrounds and skill sets. Despite its perceived exclusivity, the space industry is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses a broad range of professions, from satellite design and space tourism to climate monitoring and asteroid mining.
 As we become increasingly reliant on space-based technologies in our daily lives, the demand for professionals in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) is only set to grow. The applications of space technology are ubiquitous and diverse, from weather forecasting and GPS navigation to telecommunications and environmental monitoring. Therefore, pursuing a career in STEM is not only an excellent way to be a part of an exciting and ground-breaking industry but also a smart career choice for the future.
As we become increasingly reliant on space-based technologies in our daily lives, the demand for professionals in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) is only set to grow. The applications of space technology are ubiquitous and diverse, from weather forecasting and GPS navigation to telecommunications and environmental monitoring. Therefore, pursuing a career in STEM is not only an excellent way to be a part of an exciting and ground-breaking industry but also a smart career choice for the future.
The space industry is not limited to a select few professions, such as astronauts and rocket scientists. Rather, it offers a vast range of opportunities that are not often highlighted. For instance, space tourism is a rapidly growing field that requires professionals in hospitality, marketing, and event management, among others. With technological advancements such as reusable rockets and miniaturized satellites, new avenues for exploration and innovation are opening up, providing even more opportunities for STEM professionals.
Space is a Growing Market
The space sector is one of the fastest growing industries globally – it’s predicted to be worth $3 trillion by 2040.
That’s:
- 20 x the size of the whole Video game industry
- 15 x the size of the whole supermarket industry
- 150 x the value of Chelsea Football club – the richest club in the world!

The scale of growth in the space market is staggering. The global space economy grew by 6.7 % on average per year between 2005 and 2017, almost twice the 3.5 % average yearly growth of the global economy.
One of the main drivers of this growth is the emergence of NewSpace companies. These are privately funded startups that are leveraging cutting-edge technology and innovative business models to disrupt the traditional space industry. Unlike traditional space companies, NewSpace firms are more agile and can quickly adapt to changing market conditions. They are also more cost-effective, thanks to advancements in technology that have made it possible to produce spacecraft and launch vehicles at a fraction of the cost.
NewSpace companies are involved in a wide range of activities, from building and launching satellites to providing space-based services such as Earth observation, telecommunications, and navigation.
NewSpace companies have brought innovation, agility, and cost-effectiveness to the sector, driving unprecedented growth and new opportunities. The emergence of NewSpace companies has brought a new level of excitement and optimism to the space industry. These companies are leveraging technology and innovative business models to create new opportunities and drive unprecedented growth. As the industry continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see more NewSpace companies emerge, further fueling the growth of this exciting and rapidly expanding market.
What is the Space Sector?
The space sector, also known as the space industry, refers to the collection of businesses, organizations, and agencies involved in the research, development, manufacturing, and operation of space-related technologies and activities. The sector encompasses a wide range of fields, from space exploration and satellite communications to space tourism and space-based scientific research.
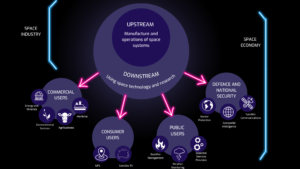
The space sector is divided into two main categories: upstream and downstream.
Upstream space activities include the design, development, and manufacturing of spacecraft, launch vehicles, and space-related technologies. This includes everything from designing and building rockets to developing and testing new materials and technologies for space exploration.
Downstream space activities are focused on using space-based technologies and data to solve problems on Earth. This includes satellite-based communications, remote sensing, satellite navigation, and space-based scientific research.
That data can be used in a number of different ways:
-
Commercial usage
Commercial applications of space technologies include satellite communications, remote sensing, and satellite navigation. These technologies are used in a wide range of industries, from telecommunications and transportation to agriculture and natural resources management.
-
Consumer usage
Consumer applications of space technologies include satellite television and satellite-based internet services. These technologies provide high-speed connectivity to people in remote areas where traditional internet services are not available.
-
Public Users
Public applications of space technologies include weather forecasting, disaster response, and scientific research. Satellites are used to track weather patterns, monitor natural disasters, and study Earth’s environment, climate, and natural resources.
-
Defence & security
Satellite data is used to keep us all safe. Security and defence applications of space technologies include satellite imagery and communications for military purposes, as well as missile defence systems and space-based early warning systems.
NewSpace vs Old Space
The space sector is also made up of NewSpace companies and Old Space organisations. NewSpace companies are independent and privately owned and funded. There’s been an absolute explosion of NewSpace companies that have started since the turn of the millennium and many of them are driving innovation in the sector. Since 2000, the Space sector has attracted at least €150 billion of private investment every year.
Old Space are the organisations we know and love. Old Space refers to the traditional space industry that has been dominated by government agencies and large aerospace corporations, such as NASA, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin. These companies have been at the forefront of space exploration and have developed many of the technologies and capabilities that we use today, such as the International Space Station (ISS) and the Space Shuttle.
While Old Space has been dominant for many decades, the emergence of NewSpace has led to significant changes in the industry. NewSpace companies are more innovative, collaborative, and focused on commercial applications of space technology. They have opened up opportunities for new players to enter the industry and have driven down costs, making space exploration more accessible to a wider range of stakeholders.
From a business perspective, NewSpace represents a significant opportunity for entrepreneurs and investors who are looking to capitalize on the growing demand for space-based services and technologies. As the industry continues to evolve, there will be many opportunities for new players to enter the market and carve out a niche for themselves.
Where on Earth?
Whist the US leads the way with over half the space companies being based here, many other countries are emerging as big players in the space sector. 40% of the world’s countries have space businesses of some type and there are a reported 10,000 space tech companies you could work for! With the Space sector, you can truly work anywhere in the world – and beyond it.
72 nations now have a space programme including European Space Agency, NASA and the UK Space Agency.
The space industry is a global one, with companies and organizations located in every corner of the world. From North America to Europe, Asia, Africa, and South America, each region has a unique set of companies and space programs that contribute to the overall growth and development of the industry. As the space industry continues to grow and evolve, we can expect to see more companies and organizations from all around the world emerging as key players. Each region brings its unique set of strengths, challenges, and opportunities, making the industry truly global in nature.
Want to know more? Find out about the growth of the Geospatial Industry here.
Careers in the Space Sector
With a rapid growth in the industry, there are now more career opportunities than ever for those seeking to start a career in space-related fields. However, with such a diverse range of career opportunities on offer, it can be challenging to know where to begin.
There are two main routes into any sector 1. Education and 2. Experience
Education
The most traditional route into the sector is through STEM subjects, but any qualification will allow some form of entry into the sector. Continue with Physics and Maths, and Engineering at secondary level if you can. A traditional route is to focus on these and then go on to study Maths, Physics, Computer Science, Astrophysics, Materials Science or Engineering (Aerospace, Electronic and Mechanical) at university. But don’t forget the other subjects – Politics, Business, Law and Communication all play a part in current space roles. Geography can be applied to Geology and Planetary Science; Psychology is useful in assessing the impact of space travel on the human mind, Earth Observation Science uses Biology and Chemistry.
The educational requirements for a career in the space sector depend on the specific field you wish to pursue. For instance, engineers and scientists typically require a Bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as aerospace engineering or physics. However, certain positions may require a Master’s or Ph.D. degree in a specialized field.
For those interested in space law or space policy, a degree in law or public policy is typically required. Additionally, for those interested in space business and management positions, a degree in business administration or management may be required.
Experience
Experience is another crucial factor when it comes to careers in the space sector. Many companies prefer candidates who have experience in related fields, such as aerospace engineering or astrophysics. Internships or co-op programs can also provide valuable experience and help candidates stand out when applying for jobs in the space industry.
Not every job in the space sector will require you to have a degree, and don’t think the door will be closed if you choose not to get one. There are some fabulous ways to grow your experience so companies will take you seriously. From Competitions and Hackathons to just volunteering – all give you valuable experience that an employer will recognise.
Apply to internships and placements, join space communities, enter competitions and hackathons and register to dedicated recruitment companies like EVONA. Attend as many space events as you can – if you can’t afford the ticket consider volunteering. A lot are taking place online currently so it’s a good time to go to as many as possible. Science and engineering STEM Ambassadors from companies like Airbus and Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) run workshops at secondary schools regularly so do your homework and find out about opportunities near you.
Routes into the Space Sector
The space sector offers a variety of routes into the industry, including:
- Internships and Co-op Programs – Many companies in the space industry offer internships and co-op programs for students and recent graduates. These programs provide valuable experience and can help candidates get their foot in the door.
- Military – Military experience can also be valuable for those interested in a career in the space industry. Many military personnel have experience in related fields, such as aerospace engineering or electronics, and the military also operates many space-related programs.
- Education – Pursuing a degree in a relevant field, such as aerospace engineering or physics, is a common route into the space sector. Advanced degrees, such as a Master’s or Ph.D., may also be required for certain positions.
- Transferable Skills – Many skills that are valuable in the space industry, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and attention to detail, can be developed in other industries. Candidates with transferable skills may be able to transition into a career in the space sector.
Tips for Starting a Career in the Space Sector
- Research Companies – Researching companies in the space industry is a crucial first step when starting a career in the sector. Candidates should look for companies that align with their interests and values and have a reputation for innovation and excellence.
- Build a Network – Building a network is also crucial when starting a career in the space sector. Candidates should attend industry events and conferences and connect with professionals in the field. Joining industry-related organizations, such as the National Space Society or the American Astronautical Society, can also help build a network of contacts.
- Develop Transferable Skills – Developing transferable skills, such as problem-solving and critical thinking, can make candidates more attractive to potential employers in the space industry. Candidates should also work on developing strong communication and teamwork skills, as collaboration is essential in many roles within the industry.
- Pursue Relevant Education and Training – Pursuing relevant education and training, such as a degree in aerospace engineering or a related field, can help candidates stand out when applying for jobs in the space industry. Candidates should also consider pursuing certifications in relevant areas, such as project management or quality assurance.
- Stay Current with Industry Developments – The space sector is a rapidly evolving industry, and it’s essential for candidates to stay up to date with the latest developments and trends. Candidates should read industry publications, attend industry events, and follow industry leaders on social media to stay informed.
- Be Flexible and Adaptable – The space sector is a dynamic and fast-paced industry, and candidates should be prepared to be flexible and adaptable in their careers. This may involve working in different roles or locations, taking on new challenges, and continually learning and developing new skills.
We’ve put together a list of resources at the bottom of this blog post to help and a free downloadable guide with EVEN MORE links, tips and hints.
What kind of roles are there in space?
Engineers: Mechanical Engineers, Electronic Engineers responsible for the design and manufacture of spacecraft, satellites and related instrumentation.
IT: Software Engineers, Mathematicians and Data Analysts responsible for the development and implementation of software to control and monitor spacecraft and analyse data for weather, navigation and communications purposes.
Scientists: Geologist, Physicists, Biologists, Climatologists, Chemists and Space Medics, designing experiments and analysing space and satellite data.
Non-Technical careers: These include sales, public relations, business strategy, educational outreach, insurance, journalism, law and even tourism.
Where are the growth areas in the Space Sector?
New Space is growing rapidly with these areas seeing excelled levels of growth to date.
The space sector has witnessed tremendous growth in the last decade, and this trend is set to continue in the coming years. With the advent of New Space, there has been a democratization of the industry, and several new players have entered the arena. The space sector is no longer the exclusive domain of government agencies and large corporations; today, innovative startups and entrepreneurial ventures are leading the way in developing new technologies and services. In this article, we will explore the growth areas in the space sector, with a focus on New Space.

-
Earth Observation Systems
Earth observation systems involve the use of satellites to monitor and study the planet’s natural and built environment. These systems provide valuable data and insights to governments, businesses, and individuals in several areas such as agriculture, mining, and natural resource management. With the growing demand for high-resolution imagery and real-time data, the market for earth observation systems is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Satellite Manufacturing
Satellite manufacturing involves the design, development, and production of satellites for various applications such as communication, navigation, and earth observation. With the increasing demand for satellite services and the emergence of new markets, the satellite manufacturing industry is poised for significant growth in the coming years.
-
Communication & Navigation
Communication and navigation are critical components of the space sector. The development of new technologies such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) has increased the demand for high-speed connectivity and reliable navigation systems. The market for communication and navigation services is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with several new players entering the market.
-
Innovative Launch Systems
Innovative launch systems involve the development of new launch technologies and services that provide cost-effective and efficient access to space. With the emergence of reusable launch vehicles and small satellite launchers, the market for innovative launch systems is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Debris & Waste Management
Debris and waste management involve the development of technologies and services that help manage the increasing amount of space debris and waste generated by human activities in space. With the growing concern over the impact of space debris on satellite operations and the risk of collisions, the market for debris and waste management is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Space Tourism
Space tourism involves the provision of commercial space travel services to individuals for recreational purposes. With the emergence of new players such as Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, the space tourism market is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Exploration
Exploration involves the study and exploration of space and celestial bodies such as planets, asteroids, and comets. With the increasing interest in space exploration and the emergence of new technologies such as robotic missions, the market for exploration is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Medicine
Medicine involves the development of technologies and services that help address health and medical issues related to human spaceflight. With the growing interest in long-duration space missions and the potential for space-based medical research, the market for space medicine is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Food & Nutrition
Food and nutrition involve the development of technologies and services that help address the challenges of providing nutritious and safe food for human spaceflight. With the growing interest in long-duration space missions and the potential for space-based agriculture, the market for food and nutrition is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Material & Design
Material and design involve the development of new materials and design concepts for space applications. With the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials and the emergence of new design tools and technologies, the market for material and design is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Law & Space Policy
Law and space policy involve the development of legal and regulatory frameworks for space activities. With the growing interest in space activities and the increasing number of players in the industry, there is a need for robust and effective legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure the safe, sustainable, and responsible use of space. The market for law and space policy services is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
-
Mining
Mining involves the exploration and extraction of natural resources from celestial bodies such as the Moon, asteroids, and comets. With the increasing interest in space resource utilization and the potential for space-based mining operations, the market for mining is set to grow significantly in the coming years.
Start your career in space – Links (UK)
The Satellite Applications Catapult
UK Space Agency’s Space Placements in INdustry scheme (SPIN)
Engineering Development Trust – Year in Industry
European Space Agency – Internships
The Royal Aeronautical Society
British Interplanetary Society
The Royal Astronomical Society
The UK Students for the Exploration and Development of Space (UKSEDS)
Space Schools
Competitions & Hackathons
NASA’ s International Space Applications Challenge
The Ukayroc Rocketry Challenge
The UK Space Agency’s SatelLife Competition (2020, future comps TBA)
EVONA Resources
EVONA’s Space Sector Student Guide

-
How to Deal with Change at Work
Learn how to deal with change at work, transforming it from a hurdle into a catalyst for personal and professional growth.Read More -
The Best STEM Books for Children
STEM subjects are a crucial part children's education whilst growing up, however, when they are at such a young age it can be hard to know how to introduce STEM to your children at home.Read More -
Project Inclusivity Drives Diversity – White House Edition
Discover Project IDD: White House Edition, a trilogy empowering space sector equality with key insights & tools for fostering diversity & inclusion.Read More